Inspect 'Windows Device Manager' again - a new interface 'USB Serial Interface' would show up after the driver was changed. It should be missing a driver. Refer to picture '4'. Point the new interface manually to 'ftdiport.inf' located again in the folder where you extracted the driver (like you did in step 4 but for a different inf file. Improvements and fixes. This update includes a fix for an incorrect device driver (“Microsoft – WPD – 2/22/2016 12:00:00 AM - 5.2.5326.4762”) that was released by a third-party on March 8, 2017 that affected a small group of users with USB connected phones or other media devices that rely on Media Transfer Protocol (MTP).
-->Important
This topic is for programmers. If you are a customer experiencing USB problems, see Troubleshoot common USB problems
This topic lists the Microsoft-provided drivers for the supported USB device classes.
- Microsoft-provided drivers for USB-IF approved device classes.
- For composite devices, use USB Generic Parent Driver (Usbccgp.sys) that creates physical device objects (PDOs) for each function.
- For non-composite devices or a function of a composite device, use WinUSB (Winusb.sys).
If you are installing USB drivers: You do not need to download USB device class drivers. They are installed automatically. These drivers and their installation files are included in Windows. They are available in the WindowsSystem32DriverStoreFileRepository folder. The drivers are updated through Windows Update.
If you are writing a custom driver: Before writing a driver for your USB device, determine whether a Microsoft-provided driver meets the device requirements. If a Microsoft-provided driver is not available for the USB device class to which your device belongs, then consider using generic drivers, Winusb.sys or Usbccgp.sys. Write a driver only when necessary. More guidelines are included in Choosing a driver model for developing a USB client driver.

USB Device classes
USB Device classes are categories of devices with similar characteristics and that perform common functions. Those classes and their specifications are defined by the USB-IF. Each device class is identified by USB-IF approved class, subclass, and protocol codes, all of which are provided by the IHV in device descriptors in the firmware. Microsoft provides in-box drivers for several of those device classes, called USB device class drivers. If a device that belongs to a supported device class is connected to a system, Windows automatically loads the class driver, and the device functions with no additional driver required.
Hardware vendors should not write drivers for the supported device classes. Windows class drivers might not support all of the features that are described in a class specification. If some of the device's capabilities are not implemented by the class driver, vendors should provide supplementary drivers that work in conjunction with the class driver to support the entire range of functionality provided by the device.
For general information about USB-IF approved device classes see the USB Common Class Specification

The current list of USB class specifications and class codes is documented in the USB-IF Defined Class Code List.

Device setup classes
Windows categorizes devices by device setup classes, which indicate the functionality of the device.
Microsoft defines setup classes for most devices. IHVs and OEMs can define new device setup classes, but only if none of the existing classes apply. For more information, see System-Defined Device Setup Classes.
Two important device setup classes for USB devices are as follows:
USBDevice {88BAE032-5A81-49f0-BC3D-A4FF138216D6}: IHVs must use this class for custom devices that do not belong to another class. This class is not used for USB host controllers and hubs.
USB {36fc9e60-c465-11cf-8056-444553540000}: IHVs must not use this class for their custom devices. This is reserved for USB host controllers and USB hubs.
The device setup classes are different from USB device classes discussed earlier. For example, an audio device has a USB device class code of 01h in its descriptor. When connected to a system, Windows loads the Microsoft-provided class driver, Usbaudio.sys. In Device Manager, the device is shown under is Sound, video and game controllers, which indicates that the device setup class is Media.
Microsoft-provided USB device class drivers
| USB-IF class code | Device setup class | Microsoft-provided driver and INF | Windows support | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Audio (01h) | Media {4d36e96c-e325-11ce-bfc1-08002be10318} | Usbaudio.sys Wdma_usb.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions (Home, Pro, Enterprise, and Education) Windows 10 Mobile Windows 8.1 Windows 8 Windows 7 Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista | Microsoft provides support for the USB audio device class by means of the Usbaudio.sys driver. For more information, see 'USBAudio Class System Driver' in Kernel-Mode WDM Audio Components. For more information about Windows audio support, see the Audio Device Technologies for Windows website. |
| Communications and CDC Control (02h) | ||||
| Ports {4D36E978-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318} | Usbser.sys Usbser.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 10 Mobile | In Windows 10, a new INF, Usbser.inf, has been added that loads Usbser.sys automatically as the function driver. For more information, see USB serial driver (Usbser.sys) | |
| Modem {4D36E96D-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318} Note Supports Subclass 02h (ACM) | Usbser.sys Custom INF that references mdmcpq.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 8.1 Windows 8 Windows 7 Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista | In Windows 8.1 and earlier versions, Usbser.sys is not automatically loaded. To load the driver, you need to write an INF that references the modem INF (mdmcpq.inf) and includes [Install] and [Needs] sections. Starting with Windows Vista, you can enable CDC and Wireless Mobile CDC (WMCDC) support by setting a registry value, as described in Support for the Wireless Mobile Communication Device Class. When CDC support is enabled, the USB Common Class Generic Parent Driver enumerates interface collections that correspond to CDC and WMCDC Control Models, and assigns physical device objects (PDO) to these collections. | |
| Net {4d36e972-e325-11ce-bfc1-08002be10318} Note Supports Subclass 0Eh (MBIM) | wmbclass.sys Netwmbclass.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 8.1 Windows 8 | Starting in Windows 8, Microsoft provides the wmbclass.sys driver, for mobile broadband devices. See, MB Interface Model. | |
| HID (Human Interface Device) (03h) | HIDClass {745a17a0-74d3-11d0-b6fe-00a0c90f57da} | Hidclass.sys Hidusb.sys Input.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 10 Mobile Windows 8.1 Windows 8 Windows 7 Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista | Microsoft provides the HID class driver (Hidclass.sys) and the miniclass driver (Hidusb.sys) to operate devices that comply with the USB HID Standard. For more information, see HID Architecture and Minidrivers and the HID class driver. For further information about Windows support for input hardware, see the Input and HID - Architecture and Driver Support website. |
| Physical (05h) | - | - | - | Recommended driver: WinUSB (Winusb.sys) |
| Image (06h) | Image {6bdd1fc6-810f-11d0-bec7-08002be2092f} | Usbscan.sys Sti.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 8.1 Windows 8 Windows 7 Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista | Microsoft provides the Usbscan.sys driver that manages USB digital cameras and scanners for Windows XP and later operating systems. This driver implements the USB component of the Windows Imaging Architecture (WIA). For more information about WIA, see Windows Image Acquisition Drivers and the Windows Imaging Component website. For a description of the role that Usbscan.sys plays in the WIA, see WIA Core Components. |
| Printer (07h) | USB Note Usbprint.sys enumerates printer devices under the device set up class: Printer {4d36e979-e325-11ce-bfc1-08002be10318}. | Usbprint.sys Usbprint.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 8.1 Windows 8 Windows 7 Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista | Microsoft provides the Usbprint.sys class driver that manages USB printers. For information about implementation of the printer class in Windows, see the Printing - Architecture and Driver Support website. |
| Mass Storage (08h) | ||||
| USB | Usbstor.sys | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 10 Mobile Windows 8.1 Windows 8 Windows 7 Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista | Microsoft provides the Usbstor.sys port driver to manage USB mass storage devices with Microsoft's native storage class drivers. For an example device stack that is managed by this driver, see Device Object Example for a USB Mass Storage Device. For information about Windows storage support, see the Storage Technologies website. | |
| SCSIAdapter {4d36e97b-e325-11ce-bfc1-08002be10318} | SubClass (06) and Protocol (62) Uaspstor.sys Uaspstor.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 10 Mobile Windows 8.1 Windows 8 | Uaspstor.sys is the class driver for SuperSpeed USB devices that support bulk stream endpoints. For more information see: | |
| Hub (09h) | USB {36fc9e60-c465-11cf-8056-444553540000} | |||
| Usbhub.sys Usb.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 10 Mobile Windows 8.1 Windows 8 Windows 7 Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista | Microsoft provides the Usbhub.sys driver for managing USB hubs. For more information about the relationship between the hub class driver and the USB stack, see USB host-side drivers in Windows. | ||
| Usbhub3.sys Usbhub3.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 8.1 Windows 8 | Microsoft provides the Usbhub3.sys driver for managing SuperSpeed (USB 3.0) USB hubs. The driver is loaded when a SuperSpeed hub is attached to an xHCI controller. See USB host-side drivers in Windows. | ||
| CDC-Data (0Ah) | - | - | - | Recommended driver: WinUSB (Winusb.sys) |
| Smart Card (0Bh) | SmartCardReader {50dd5230-ba8a-11d1-bf5d-0000f805f530} | |||
| Usbccid.sys (Obsolete) | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 7 Windows Server 2008 Windows Vista | Microsoft provides the Usbccid.sys mini-class driver to manage USB smart card readers. For more information about smart card drivers in Windows, see Smart Card Design Guide. Note that for Windows Server 2003, Windows XP, and Windows 2000, special instructions are required for loading this driver because it might have been released later than the operating system. Note Usbccid.sys driver has been replaced by UMDF driver, WUDFUsbccidDriver.dll. | ||
| WUDFUsbccidDriver.dll WUDFUsbccidDriver.inf | Windows 8.1 Windows 8 | WUDFUsbccidDriver.dll is a user-mode driver for USB CCID Smart Card Reader devices. | ||
| Content Security (0Dh) | - | - | - | Recommended driver: USB Generic Parent Driver (Usbccgp.sys). Some content security functionality is implemented in Usbccgp.sys. See Content Security Features in Usbccgp.sys. |
| Video (0Eh) | Image {6bdd1fc6-810f-11d0-bec7-08002be2092f} | Usbvideo.sys Usbvideo.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows Vista | Microsoft provides USB video class support by means of the Usbvideo.sys driver. For more information, see 'USB Video Class Driver' under AVStream Minidrivers. Note that for Windows XP, special instructions are required for loading this driver because it might have been released later than the operating system. |
| Personal Healthcare (0Fh) | - | - | - | Recommended driver: WinUSB (Winusb.sys) |
| Audio/Video Devices (10h) | - | - | - | - |
| Diagnostic Device (DCh) | - | - | - | Recommended driver: WinUSB (Winusb.sys) |
| Wireless Controller (E0h) Note Supports Subclass 01h and Protocol 01h | Bluetooth {e0cbf06c-cd8b-4647-bb8a-263b43f0f974} | Bthusb.sys Bth.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 10 Mobile Windows 8.1 Windows 8 Windows 7 Windows Vista | Microsoft provides the Bthusb.sys miniport driver to manage USB Bluetooth radios. For more information, see Bluetooth Design Guide. |
| Miscellaneous (EFh) | Net {4d36e972-e325-11ce-bfc1-08002be10318} Note Supports SubClass 04h and Protocol 01h | Rndismp.sys Rndismp.inf | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 8.1 Windows 8 Windows 7 Windows Vista | Prior to Windows Vista, support for CDC is limited to the RNDIS-specific implementation of the Abstract Control Model (ACM) with a vendor-unique protocol (bInterfaceProtocol) value of 0xFF. The RNDIS facility centers the management of all 802-style network cards in a single class driver, Rndismp.sys. For a detailed discussion of remote NDIS, see Overview of Remote NDIS. The mapping of remote NDIS to USB is implemented in the Usb8023.sys driver. For further information about networking support in Windows, see the Networking and Wireless Technologies website. |
| Application Specific (FEh) | - | - | - | Recommended driver: WinUSB (Winusb.sys) |
| Vendor Specific (FFh) | - | - | Windows 10 for desktop editions Windows 10 Mobile | Recommended driver: WinUSB (Winusb.sys) |
Related topics
≡Low-cost high-speed ARM USB JTAG (supported by the OpenOCD arm debugger)| Price | 39.95EUR |
|---|---|
| 10 - 49 pcs | 35.96EUR |
| 50 - 10000 pcs | 31.96EUR |
FEATURES
Olimex Usb Devices Driver Win 7
- Debugs all ARM microcontrollers with JTAG interface supported by OpenOCD
- High speed USB 2.0 with lower latency time, RTCK adaptive JTAG clock up to 30Mhz and higher throughput achieve x3-x5 times faster programming speed than ARM-USB-TINY, can be used with all ARM devices for programming and debugging.
- Uses ARM's standard 2x10 pin JTAG connector
- Supports ARM targets working in voltage range 2.0 – 5.0 V DC
- Supported by the open-source community and OpenOCD debugger software
- Downloadable Windows installer for full featured and open source tools as alternative to the commercial ARM development packages: GCC C compiler, openOCD debugger and Eclipse IDE.
- Works with IAR EW for ARM via GDB server
- Works with Rowley Crossworks IDE
- Works with CooCox IDE
- Supported in Windows, Linux and Mac
- Dimensions 50x40 mm (2x1.6') + 20 cm (8') JTAG cable - ribbon cable included
HARDWARE
SOFTWARE
- Additional resources: tutorials, instructions, demo software, customer projects, older drivers and more might be found at the wiki page: ARM-USB-TINY article
/20161803_iphone6s_stealth_black_full_open_3_render-583dceb65f9b58d5b134f4d8.jpg)
FAQ
- Can I use ARM-USB-TINY with EW-ARM?
- IAR EW has support for GDB and works with ARM-USB-TINY-H.
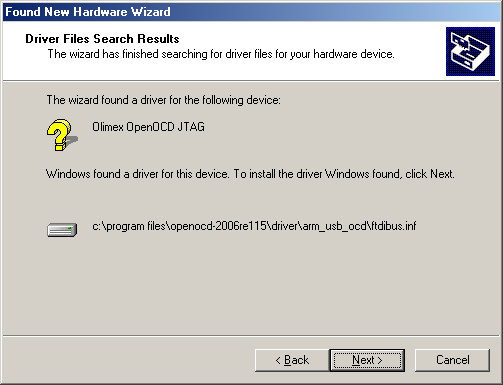
- I am currently using operating system X. It has FTDI drivers, how should I alter them to work with my installation?
- FTDI provide drivers and instructions at their web site, download them and use our ARM-USB-TINY-H PID: 0x002a, VID: 0x15BA to install the drivers.
- I have LPC1227 board and can't program it with your OpenOCD debugger. What do I do wrong?
- LPC1227 lacks JTAG according to the microcontroller's datasheet. The board can be programmed only via SWD (Serial Wire Debug) interface. Olimex OpenOCD debuggers have JTAG by default. You would need an addiitonal adapter – ARM-JTAG-SWD.
- How to install ARM-USB-TINY to work with CrossWorks:
Test with the FTDI drivers. The FTDI drivers can be downloaded from the following address:
https://www.olimex.com/Products/ARM/JTAG/_resources/OLIMEX-FTDI-drivers-2-12-04.zip
There is profile for ARM-USB-TINY in CrossWorks, but if you want to use 'Generic FTD2232' target interface you have to do as follows:- Right click on a blank space in the targets window and select 'New Target Interface > Generic FT2232 Device'.
- Right click on the new target interface and select 'Properties' - set the following properties:
Connected LED Inversion Mask 0x0000
Connected LED Mask = 0x0800
nSRST Inversion Mask = 0x0200
nSRST Mask = 0x0200
nTRST Inversion Mask = 0x0000
nTRST Mask = 0x0100
Output Pins = 0x0F1B
Output Value = 0x0D08
Running LED Inversion Mask = 0x0000
Running LED Mask = 0x0800
PID: 0x002a
VID: 0x15baIn CrossWorks 1.7 there are Target interfaces for Olimex JTAGs, note that RTCK is not used with a FT2232 design so your JTAG clock should not exceed 1/6 of your target MCU clock or the JTAG will lock up. Start with JTAG divider 10 and decrease until you are able to debug to find your own value for your target.
- What is the difference between ARM-USB-OCD and ARM-USB-TINY?
- ARM-USB-TINY is stripped down version of ARM-USB-OCD, the differences are: no output buffers just current limitation resistor protectors, no RS232, no additional power supply for the target.
- Can I debug high voltage targets with ARM-USB-TINY?
- ARM-USB-TINY is not isolated, but you can use USB-ISO isolator device to protect your PC while debugging high voltage targets.
- Howdy, guys. I can't program my MSP430 and PIC16 boards with your robust debugger. I need help ASAP.
- Technically, it is possible to program targets different than ARM using our OpenOCD debugger. Practically, almost all users use the debugger for ARM programming and only ARM targets are officially supported. There is a reason that the prefix in the name of the debugger is 'ARM-'.
- I am the maintainer of a commercial IDE with custom debugger code. I want to include support for your OpenOCD tools in my software, however I can't find specific information. It is obviously a win-win situation for both parties. Is it possible to provide me with more specific technical information for your debuggers?
- Olimex can provide the necessary information and cooperate with interested parties if they want to add low-cost USB debugger support to their C compilers and IDEs.
Related Products - People who bought this product also bought
ARM debugger with JTAG and SWD interfaces, based on CoLinkEX
Olimex Usb Devices Driver Vga
High-speed 3-IN-1 fast USB ARM JTAG, USB-to-RS232 virtual port and power supply 5VDC device (supported by OpenOCD arm debugger)